Development of the Human Nervous System
-
Begins: Day 15 post-conception (p/c).
-
Formation of primitive streak of specialized neuroectoderm on embryo’s dorsal surface.
Hensen’s Node and Neural Plate
-
Hensen’s node: Small nodule at rostral end of neural plate.
-
Directs development of the anterior neural tube.
-
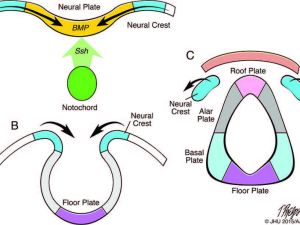 Development of the neural tube and neural crest. Fig. A shows the action of dorsalising signals from the ectoderm (e.g. bone morphogenetic proteins; BMP) and ventralising signals (e.g. sonic hedgehog, SHH) from the notochord on the developing neural plate. Fig. B shows folding of the edges of the neural plate to form the neural tube. Fig. C shows covering by the mesoderm and ectoderm over the closed neural tube, and separation of the neural crest tissues. The neural tube divided by the sulcus limitans into the dorsal alar and roof plates, and the ventral basal and floor plates. (Adapted from Ten Donkelaar, et al. Clinical Neuroembryology, 2nd edition, Springer 2014.)
Development of the neural tube and neural crest. Fig. A shows the action of dorsalising signals from the ectoderm (e.g. bone morphogenetic proteins; BMP) and ventralising signals (e.g. sonic hedgehog, SHH) from the notochord on the developing neural plate. Fig. B shows folding of the edges of the neural plate to form the neural tube. Fig. C shows covering by the mesoderm and ectoderm over the closed neural tube, and separation of the neural crest tissues. The neural tube divided by the sulcus limitans into the dorsal alar and roof plates, and the ventral basal and floor plates. (Adapted from Ten Donkelaar, et al. Clinical Neuroembryology, 2nd edition, Springer 2014.)
-
Dorsal Induction:
-
Formation and closure of neural tube.
-
Creation of three primary vesicles at rostral neural tube end.
-
-
Ventral Induction:
-
Formation of cerebral hemispheres, eye vesicles, olfactory bulbs, pituitary gland, and facial structures.
-
Primary Neurulation
-
Timeline:
-
Neural plate formation: Day 17 p/c.
-
Neural plate complete by Day 18 p/c.
-
-
Process:
-
Neural plate edges elevate and fold, forming neural tube.
-
Influenced by inductive action of underlying notochord and chordal mesoderm.
-
-
Closure of Neural Tube:
-
Starts at future rhombencephalon on Day 20 p/c.
-
Anterior neuropore closes by Day 25 p/c.
-
Posterior neuropore closes by Day 28 p/c at upper sacral level.
-
Key Events During Neural Tube Closure
-
Disjunction:
-
Neural tube separates from surface (cutaneous) ectoderm.
-
Cutaneous ectoderm closes over midline.
-
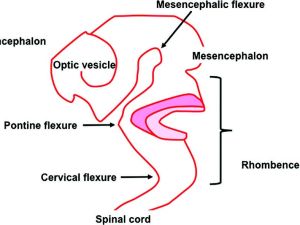 Closure of the anterior neural tube and folding into three vesicles the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephal
Closure of the anterior neural tube and folding into three vesicles the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephal
-
Mesenchymal Encirclement:
-
Neural tube surrounded by mesenchyme between tube and dermal ectoderm.
-
Mesenchyme differentiates into vertebral column, meninges, and muscle under neural tube influence.
-
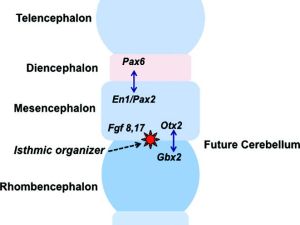 Patterning of neural territories in the anterior neural tube by organisers. Diagram showing the definition of the fundamental territories of the anterior neural tube by complex and dynamic effects of suppressor and permissive gene products. Note position of the isthmic organiser (IsO) at the mesencephalic-rhombencephalic junction, the location of the cerebellar anl
Patterning of neural territories in the anterior neural tube by organisers. Diagram showing the definition of the fundamental territories of the anterior neural tube by complex and dynamic effects of suppressor and permissive gene products. Note position of the isthmic organiser (IsO) at the mesencephalic-rhombencephalic junction, the location of the cerebellar anl
-
Impact of Failed Closure:
-
Mesenchyme exposed to internal ependymal surface of open canal differentiates into fatty tissue.
-
Basis for association of neural tube defects with lipomatous lesions.
-
-
Neural Crest Cells:
-
Formed upon neural tube closure.
-
Located dorsolaterally along neural tube.
-
Develop into dorsal root ganglia, cranial sensory, and autonomic ganglia, among other tissues.
-
Cite this: CNKE contributors.Neural tube development. CNKE.org, The Child Neurology Knowledge Environment. 17 August 2025. Available at: https://cnke.org/articles/356 Accessed 17 August 2025.

