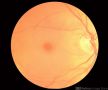
 The Cherry Red Spot refers to the appearance of a red-tinted region at the center of the macula surrounded by retinal opacification, usually present due to the thickening and loss of transparency of the posterior pole of the retina. The differential diagnosis of cherry red spot includes:
The Cherry Red Spot refers to the appearance of a red-tinted region at the center of the macula surrounded by retinal opacification, usually present due to the thickening and loss of transparency of the posterior pole of the retina. The differential diagnosis of cherry red spot includes:
Vascular causes
- Central Retinal Artery Occlusion (CRAO)
- Sudden, painless, unilateral vision loss in elderly patients.
- Cherry red spot present in 90% of permanent CRAO cases.
- Non-arteritic CRAO (95%): Caused by atherothrombosis, thromboembolism, or vasospasm.
- Thrombus sources: Carotid plaque, heart, or aorta.
- Associated with: Myxoma, cardiac valve vegetations, hypercoagulable states (e.g., hyperhomocysteinemia, factor V Leiden, protein C and S deficiencies, etc.).
- Arteritic CRAO (5%): Associated with inflammatory conditions like giant cell arteritis (GCA).
- Other causes: Susac syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, polyarteritis nodosa, granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
- Following cataract surgery (phacoemulsification) causing outer retinal whitening.
- Compromise of the choroidal and retinal circulation due to intraorbital hemorrhage or mass.
- Macular infarction due to various causes such as retinal artery and vein occlusions, carotid artery occlusions, malignant hypertension, diabetes, radiation retinopathy, posterior uveitis, systemic inflammatory vasculopathies, and trauma.
Metabolic Storage Diseases
- GM 2 gangliosidosis
- Includes Tay-Sachs disease (beta hexoaminidase A deficiency) and Sandhoff (beta hexoaminidase A+B).
- Abnormal accumulation of gangliosides in the brain and retina.
- Cherry red spot in 75-90% of early-onset cases.
- Niemann-Pick Disease
- Types A, B, C, D.
- GM1 gangliosidosis type 1
- Autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in GLB1.
- Cherry red spot in ~50% of cases.
- Sialidosis (Mucolipidosis type 1)
- Lysosomal storage disease caused by alpha-neuraminidase deficiency.
- Presents with ataxia, movement disorders, nystagmus, myoclonic seizures.
- Two types: Type I (onset in 2nd/3rd decade, gait disturbances, myoclonus, ataxia, seizures).
- Farber Disease
- Autosomal recessive disorder characterized by Ceramidase or acid ceramidase deficiency.
- Features: Painful swollen joints, subcutaneous nodules, hoarse voice, developmental delay, visceromegaly, respiratory involvement, neurological features.
- Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
- Lysosomal storage disorder due to arylsulfatase A deficiency.
- Features: Progressive intellectual and motor decline, peripheral neuropathy, hearing loss, incontinence, blindness.
- Galactosialidosis
- Autosomal recessive disorder due to mutation in CTSA gene.
- Ocular features: Cherry red spot, corneal clouding, conjunctival telangiectasia.
Inflammation
- Retinitis involving central retina
- Progressive outer retinal necrosis.
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis.
Drug Toxicity
- Quinine
- Carbon monoxide
- Dapsone poisoning
- Methanol
- Intravitreal gentamicin
Trauma
- Commotio Retinae
- Acute retinal opacification following blunt trauma (Berlin's edema).
- Optic Nerve Avulsion
- Saturday Night Retinopathy
- Occlusion of the retinal or ophthalmic artery due to prolonged prone body position.
Leukemic Infiltrates
- Infiltration of the optic nerve head causing CRAO and cherry red spot.
