The first case of Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (SJS) or chondrodystrophic myotonia was explained in 1962 by Oscar Schwartz and Robert S. Jampel in siblings with myotonic myopathy and blepharophimosis.
Classification:
- Type 1A: Recognized in childhood, moderate bone dysplasia.
- Type 1B: Similar to 1A, but manifests at birth with more prominent bone dysplasia.
- Type 2: Most severe, high neonatal mortality, also known as Stuve-Wiedemann syndrome, associated with LIFR gene mutation on chromosome 5p13.
Clinical Features
-
Common Characteristics:
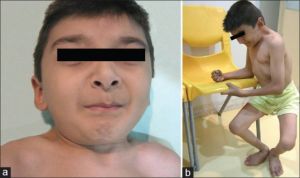 9-year-old boy with Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (Source: Basiri et al., (2015))
9-year-old boy with Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (Source: Basiri et al., (2015))- Short stature: 90%
- Clinical myotonia: 85%
- Puckered-small mouth: 80%
- Muscle hypertrophy: 70%
- Fixed facies: 55%
- Bone abnormalities: 45%
- Raised muscle enzymes: 45%
- Hip dysplasias: 40%
- Blepharophimosis and blepharospasm: 32.5%
