The first case of Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (SJS) or chondrodystrophic myotonia was explained in 1962 by Oscar Schwartz and Robert S. Jampel in siblings with myotonic myopathy and blepharophimosis.
Classification:
- Type 1A: Recognized in childhood, moderate bone dysplasia.
- Type 1B: Similar to 1A, but manifests at birth with more prominent bone dysplasia.
- Type 2: Most severe, high neonatal mortality, also known as Stuve-Wiedemann syndrome, associated with LIFR gene mutation on chromosome 5p13.
Clinical Features
-
Common Characteristics:
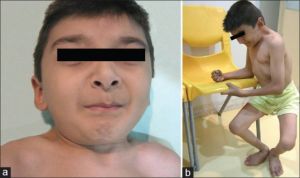 9-year-old boy with Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (Source: Basiri et al., (2015))
9-year-old boy with Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (Source: Basiri et al., (2015))- Short stature: 90%
- Clinical myotonia: 85%
- Puckered-small mouth: 80%
- Muscle hypertrophy: 70%
- Fixed facies: 55%
- Bone abnormalities: 45%
- Raised muscle enzymes: 45%
- Hip dysplasias: 40%
- Blepharophimosis and blepharospasm: 32.5%
-
Skeletal Features:
- Spinal deformities
- Fragmenting of femoral epiphysis
- Widened metaphysis
- Joint contractures
- Osteoporosis
- Delayed bone age
-
Less Common Features:
- High pitched voice
- Bilateral carpal tunnel syndromes
- Malignant hyperthermia
- Diagnostic Findings:
- Normal/slightly elevated creatine kinase and aldolase
- Normal nerve conduction studies
- Electromyography: Continuous muscle activity, high frequency repetitive potentials, myotonic discharges.
- Muscle biopsy: Nonspecific myopathic changes
- Spinal X-rays: Kyphosis and other skeletal deformities
Genetic Basis
- Inheritance: Autosomal recessive, reports of dominant inheritance.
- Mutation: HSPG2 gene on chromosome 1p34-36.1.
- Protein Affected: Perlecan, a component of basement membranes, cartilage, and bone marrow stromal cells.
Diagnosis
- Characteristic Triad: Facial dysmorphism, skeletal deformities, myotonic discharges.
- Differential Diagnosis:
- Cramp and stiffness (Stiff person syndrome, Isaac's syndrome)
- Myotonic disorders (Congenital myotonic dystrophy, myotonic dystrophy, myotonia congenita, paramyotonia congenital)
- Muscular dystrophies (Becker dystrophy, Duchenne dystrophy, congenital muscular dystrophy)
- Congenital myopathies
- Channelopathies
- Mucopolysaccharidosis (Morquio's syndrome)
- Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
- Malignant hyperthermia
- Blepharospasm
- Stuve-Wiedemann syndrome
Treatment
-
Symptomatic Management:
- Decrease abnormal muscle activity causing stiffness and cramping.
- Medications:
- Anticonvulsants: Carbamazepine, Phenytoin
- Antiarrhythmic drugs: Mexiletine, Procainamide
- Non-Pharmacologic Modalities:
- Physiotherapy
- Warming
- Massage
- Warming-up prior to exercise
- Gradual stretching
-
Surgical Interventions:
- Myectomy
- Levator resection
- Lateral canthopexy for blepharospasm and eyelid anomalies
-
Botulinum Toxin-A: Alternative treatment for blepharospasm, considered instead of surgical options (Suphatsathienkul P et al., 2024).
Conclusion
- Diagnostic Specificity: The triad of “myotonia, facial dysmorphism, and skeletal deformities” is highly specific for diagnosing SJS in children.
- Confirmative Testing: DNA testing for HSPG2 gene mutations on chromosome 1p34-36.1.
References
- Basiri K, Fatehi F, Katirji B (2015) The Schwartz-Jampel syndrome: Case report and review of literature. Adv Biomed Res 4 ():163. DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.162538 PMID: 26436077.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (Concept ID: C0036391). MedGen. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/medgen/19892. Accessed [8 June 2024].
- Suphatsathienkul P, Sakpichaisakul K, Wechapinan T, Trachoo O, Virawan S, Wanitphakdeedecha R (2024) Successful Treatment of Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome with Botulinum Toxin Type A. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 14 (2):545-556. DOI: 10.1007/s13555-023-01088-7 PMID: 38285320.
Cite this: CNKE contributors.Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome (SJS). CNKE.org, The Child Neurology Knowledge Environment. 06 July 2025. Available at: https://cnke.org/articles/328 Accessed 06 July 2025.

