Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate
Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate
- Brand Names: Vyvanse, Elvanse.
- Drug Class: Prodrug stimulant.
- Mechanism of Action:
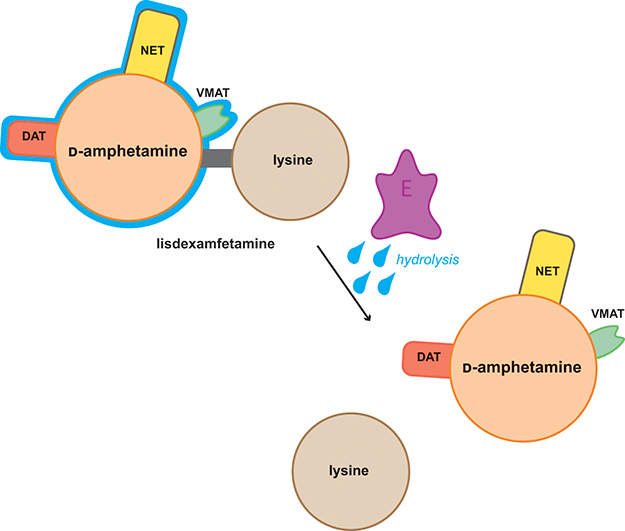
- Lisdexamfetamine is a prodrug of d-amphetamine.
- Activated enzymatically in the bloodstream to d-amphetamine.
- Increases availability of dopamine and norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft.
- Improves executive function, attention, and impulse control.
- Unique Properties:
- Requires enzymatic conversion for activation, reducing potential for abuse.
- Extended-release formulation provides sustained symptom control over 12-14 hours.
To read more, a subscription is needed: Click here to subscribe


